Introduction: The Foundation of GST Compliance
For any registered business operating under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime in India, the invoice is more than just a bill—it is the primary legal document that verifies a transaction, establishes tax liability, and, most critically, allows the recipient to claim Input Tax Credit (ITC). Given the continuous evolution of GST laws, staying updated on the precise requirements is non-negotiable.
As we look towards 2026, compliance standards are becoming stricter, especially with increased integration of e-invoicing and digital validation tools. Understanding the specific GST invoice format mandatory fields India prescribes is essential for seamless operation and avoiding penalties. If you are just starting your journey, ensuring proper GST Registration is the first crucial step toward compliance.
This comprehensive guide details every mandatory element required by law, provides actionable insights, and helps you master the compliant GST invoice format.
Why Understanding the GST Invoice Format Mandatory Fields India is Critical for ITC
The validity of an invoice directly impacts the flow of ITC across the supply chain. If an invoice is missing even one mandatory field, the recipient may be denied ITC, leading to financial loss and potential disputes with the tax authorities. Furthermore, non-compliant invoicing can trigger audits and significant penalties under the GST Act.
The Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) regularly issues notifications clarifying these requirements, emphasizing that clarity and accuracy are paramount. Adhering strictly to the prescribed GST invoice format mandatory fields India ensures that your business operates within the legal framework, protecting both you and your customers.
Legal Basis for Mandatory Invoice Fields
The rules governing the content of a tax invoice are primarily laid out in Rule 46 of the CGST Rules, 2017. These rules specify 16 essential fields that must be present on every tax invoice issued by a registered person. Failure to include these details renders the document invalid for tax purposes.
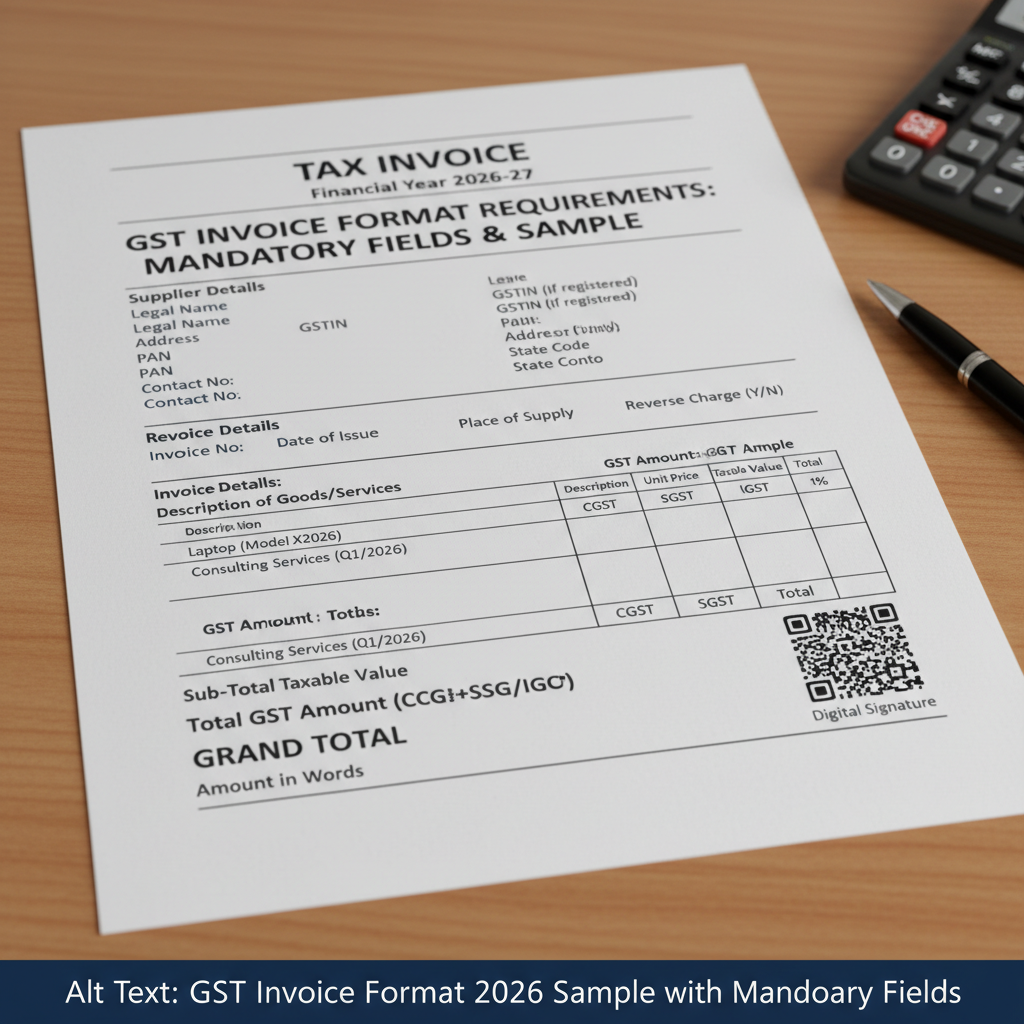
The 16 Essential GST Invoice Format Mandatory Fields India Requires
To ensure full compliance, every tax invoice must contain the following 16 mandatory particulars. These can be grouped into details related to the parties involved, the goods or services supplied, and the tax calculation:
Mandatory Fields: Supplier and Recipient Details
- Name, Address, and GSTIN of the Supplier: Essential identifying information for the invoicing entity.
- Invoice Number: A sequential, unique number (up to 16 characters) specific to the financial year.
- Date of Issue: The date when the document is generated.
- Name, Address, and GSTIN/UIN of the Recipient: If the recipient is registered.
- Name and Address of the Recipient (and Delivery Address): If the recipient is unregistered and the value exceeds ₹50,000, or if required by the recipient.
- Place of Supply (POS): Crucial for determining whether the tax is IGST, CGST, or SGST.
- Whether the Recipient is Registered or Unregistered: Required for B2C transactions exceeding specific limits.
- Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM) Applicability: Indication if tax is payable by the recipient under RCM.
Mandatory Fields: Goods/Service Details and Tax Calculation
- HSN Code (for Goods) or SAC Code (for Services): Mandatory based on turnover thresholds (detailed below).
- Description of Goods or Services: Clear specification of what is being supplied.
- Quantity and Unit (UQC): Measurement details (e.g., Kgs, Litres, Meters).
- Total Value of Supply: Taxable value of the goods or services.
- Tax Rate: Applicable rate of CGST, SGST/UTGST, or IGST.
- Amount of Tax Charged: The breakdown of tax components (e.g., CGST, SGST, IGST, Cess).
- Total Invoice Value: Value both in figures and words.
- Signature or Digital Signature of the Supplier: Authentication of the document.
Specific Requirements for HSN/SAC Codes in the GST Invoice Format Mandatory Fields India
One of the most frequently audited components of the GST invoice format mandatory fields India relates to the Harmonized System of Nomenclature (HSN) for goods and the Services Accounting Code (SAC) for services. The requirement for the number of digits in these codes is directly linked to the taxpayer’s Annual Aggregate Turnover (AATO) in the preceding financial year.
The government periodically revises the mandatory digit requirements to enhance transparency and reconciliation. As of recent updates, the general requirements are:
- AATO up to ₹5 Crore: Requires 4-digit HSN/SAC codes.
- AATO above ₹5 Crore: Requires 6-digit HSN/SAC codes.
“Accurate classification using HSN/SAC is not just a reporting requirement; it ensures the correct tax rate is applied, preventing future liability issues and ensuring proper Input Tax Credit matching,” notes a tax expert.
Invoice Types Beyond the Standard Tax Invoice
While the standard Tax Invoice is the most common document, the GST framework mandates different formats for specific scenarios. While many of the GST invoice format mandatory fields India requires remain consistent across these documents, their purpose and required headings differ significantly.
Bill of Supply
Issued by taxpayers who are under the GST Composition Scheme or those supplying exempted goods/services. Since they cannot charge tax, the tax details (rate and amount) are omitted. It must clearly state ‘Bill of Supply’.
Debit Note
Issued by the supplier when the taxable value or tax charged in the original invoice was less than the actual amount (e.g., due to price increase). It must reference the original invoice number and date.
Credit Note
Issued by the supplier when the taxable value or tax charged in the original invoice was more than the actual amount (e.g., goods returned or price reduction). It reduces the supplier’s tax liability and must reference the original invoice details.
Delivery Challan
Used for the movement of goods without sale (e.g., job work, transfer to a branch). While not a tax invoice, it still requires basic details like description, quantity, and consignor/consignee information.
Best Practices for Generating a Compliant GST Invoice Sample 2026
While Rule 46 dictates the mandatory content, there is no single prescribed physical template. Businesses have flexibility in design, provided all 16 required fields are clearly visible and legible. For the sample invoice in 2026, focus on digital readiness and clarity.
Key Design and Data Entry Considerations:
- Legibility: Ensure the font is clear and all details, especially GSTINs and HSN codes, are easily readable.
- Invoice Series: Maintain a strict, sequential series (e.g., FY2025-26/0001). Gaps or duplication can lead to audit flags.
- Tax Calculation Summary: Always provide a clear summary table showing the total taxable value, CGST, SGST, IGST, and Cess separately, leading to the grand total.
- Authorized Signatory: Ensure the invoice includes the physical or digital signature of the authorized person.
For businesses transitioning to higher turnover brackets, it is paramount to upgrade systems to handle mandatory e-invoicing requirements, which automatically validate and register the invoice with the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP). This step inherently checks most of the mandatory fields.
For further authoritative guidance on updated rules, taxpayers should always refer to the official Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) website.
Ensuring Digital Compliance and the GST Invoice Format Mandatory Fields India
In the modern GST landscape, manual invoicing is rapidly becoming obsolete, especially for medium to large enterprises. Automated accounting software provides built-in checks and balances to ensure all GST invoice format mandatory fields India dictates are included before the document is finalized.
Benefits of Using GST-Compliant Software:
Automatic HSN Validation
Software automatically pulls the correct HSN/SAC code based on the product description and validates the required digit length based on your previous year’s turnover, minimizing human error.
Accurate Tax Calculation
It calculates CGST, SGST, or IGST automatically based on the Place of Supply (POS) and the recipient’s state, preventing common errors related to interstate vs. intrastate sales.
E-Invoicing Integration
For businesses mandated to use e-invoicing, compliant software seamlessly generates the JSON file, submits it to the IRP, and receives the mandatory Invoice Reference Number (IRN) and QR code, integrating these elements into the final invoice.
Actionable Steps for Implementing the Correct GST Invoice Format Mandatory Fields India Requires
Transitioning or updating your invoicing system requires a structured approach. Ensure your team is trained and your systems are audited regularly to handle the compliance load of 2026.
- System Audit: Review your current accounting software to confirm it supports all 16 mandatory fields and the required HSN/SAC digit length based on your AATO.
- Data Verification: Cleanse your master data (customer GSTINs, product HSNs, tax rates) to ensure accuracy before generating new invoices.
- Training: Ensure all personnel involved in billing and accounts payable/receivable understand the critical importance of the date of issue, sequential numbering, and the correct Place of Supply determination.
- Template Review: Download and cross-reference your current invoice template with a verified sample to ensure no mandatory field is overlooked. Many reliable accounting platforms offer free, compliant templates.
By prioritizing accuracy in these fields, businesses significantly reduce their risk profile. Remember, the invoice is the first line of defense in tax scrutiny.
Conclusion: Mastering the Invoice for Future Growth
The complexity of the GST regime requires meticulous attention to detail, and the invoice stands as the cornerstone of compliance. By strictly adhering to the GST invoice format mandatory fields India has legislated—from the unique sequential number to the accurate HSN/SAC codes and correct tax breakdown—businesses can ensure smooth ITC flow and avoid unnecessary legal hurdles.
Regular system updates and staff training are the best investments you can make to maintain compliance in a dynamic tax environment like India. Mastering these requirements today ensures your business is robustly prepared for the digital mandates of tomorrow.
FAQs
If a mandatory field is missing, the invoice may be deemed invalid under Rule 46 of the CGST Rules. This can result in the denial of Input Tax Credit (ITC) to the recipient, leading to financial loss for them and potential liability/penalties for the supplier during an audit. It is crucial to ensure all 16 mandatory fields are present.
Generally, for B2C sales, the recipient’s GSTIN is not applicable. However, the requirement to include the recipient’s name and address becomes mandatory if the taxable value of the supply is equal to or exceeds ₹50,000, and the supply is interstate. If the value is below this threshold, the address is often optional unless required by the consumer.
For taxpayers whose Annual Aggregate Turnover (AATO) in the preceding financial year was up to ₹5 Crore, a minimum of 4 digits of the HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) code are mandatory for goods supplied on the tax invoice.
A Tax Invoice is issued by a regular GST registered taxpayer when supplying taxable goods or services and includes the calculation and charging of GST. A Bill of Supply is issued by taxpayers under the Composition Scheme or those supplying only exempted goods/services. A Bill of Supply cannot charge or show GST components.
Yes, Rule 46 permits either a physical signature or a digital signature of the supplier or their authorized representative. In the context of e-invoicing, the electronic validation through the Invoice Reference Number (IRN) and QR code often replaces the traditional physical signature requirement for specified taxpayers. For more details on compliance, refer to the official GST portal.